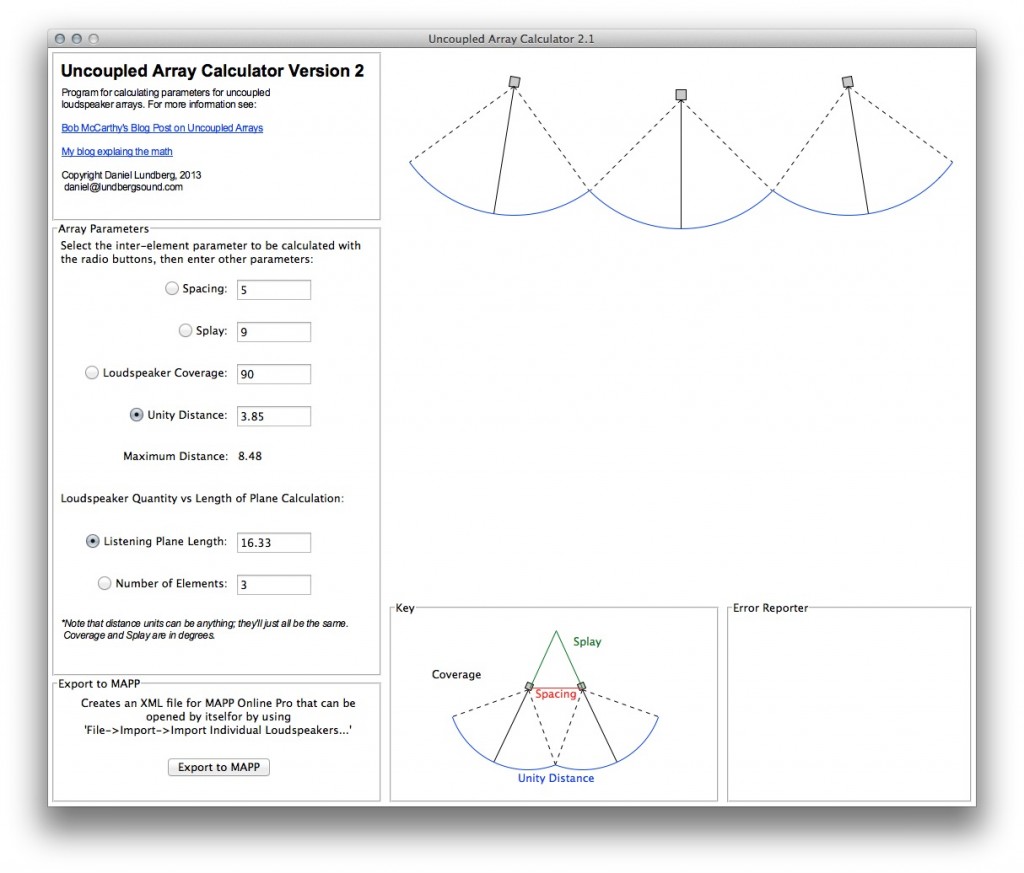
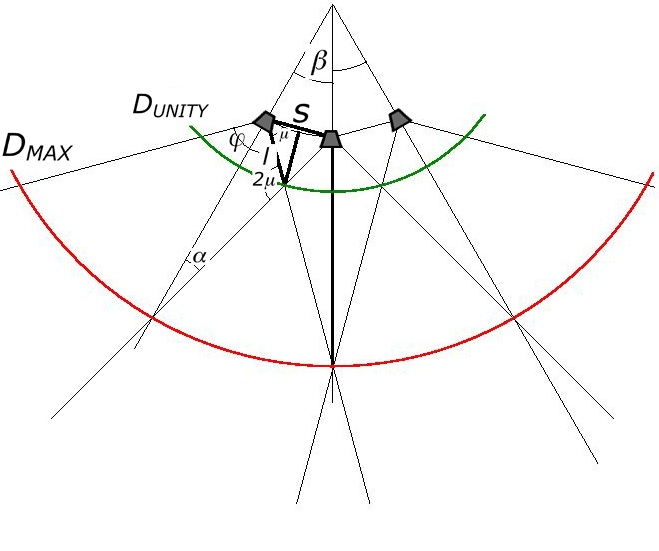
Introduction
One of the best ways to understand sound waves and phase, and how we apply them to live audio, is to see signals interact in real time on an analyzer screen while listening. This is exactly what the Meyer seminars to which I’ve been have done; the instructor sends pink noise into a DSP, has the outputs of the DSP go into a console where they can be summed, and then has the output of the console and the original noise signal go into a SIM analyzer for comparison. Attendees see the effects of summing multiple signals that differ in phase and/or amplitude, or the effects of EQs and filters, at the same time as they hear them. I’d like to share with you a simple method for having the same type of educational resource entirely inside Mac OS X – no expensive external hardware required.
It requires a dual-channel software FFT analyzer (I use SMAART 7), Apple’s AU Lab, which is a part of the developer tools package that comes with every mac, and Soundflower, a utility that allows internal routing of audio signals. I am using the signal generator inside SMAART, but you can use another program if you like. The basic routing is as follows: the signal goes into AU Lab, gets routed to several busses to which different processing can be applied and that can be summed, and goes to the measurement channel of the analyzer software where it meets up with a copy of the original signal for the transfer function. A separate output routes the processed/summed signal to the computer’s speakers so that you can listen to what you’re doing at an independent level, or not.
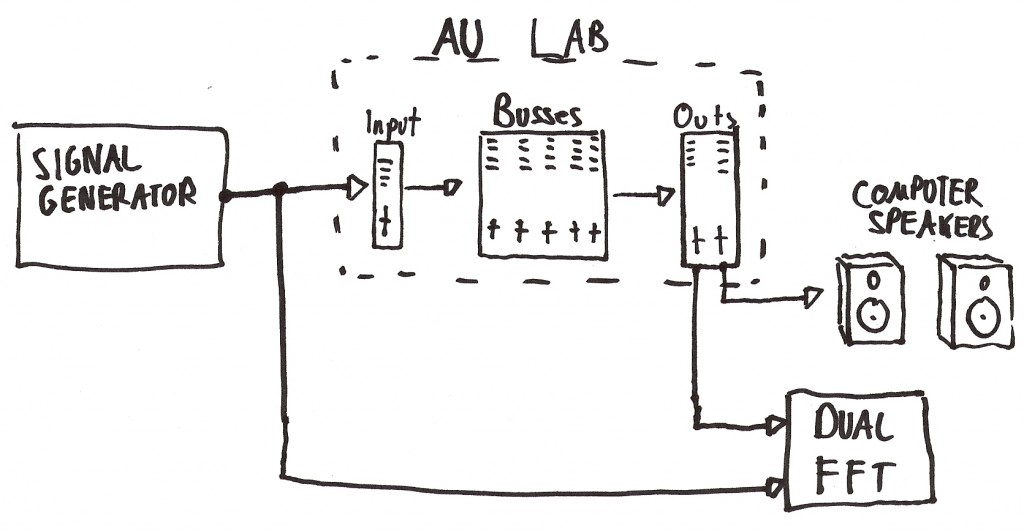
Read more